We can, of course, see the same type of arbitrage with AMMs, albeit in a slightly different form. Suppose you heard about SHIB early and you wanted to buy some before it was available on a centralized exchange. Because it’s not on an exchange you called on an Ethereum-based AMM (SHIB was created on Ethereum as an ERC-20 token), and you clicked the buttons to make your purchase of SHIB tokens. When you make that order, it gets thrown into a big batch of proposed Ethereum transactions. Some of those transactions could be people buying stuff online with USDC, but many of them are trades for tokens like SHIB or WIF or PEPE.
Related Posts

Ethereum, Solana, Doge traders caught off guard as Musk-Trump split weighs on markets
Total crypto liquidations hit $972.22 million in 24 hours, with Ethereum, XRP, Dogecoin, and Solana among the most impacted Long…
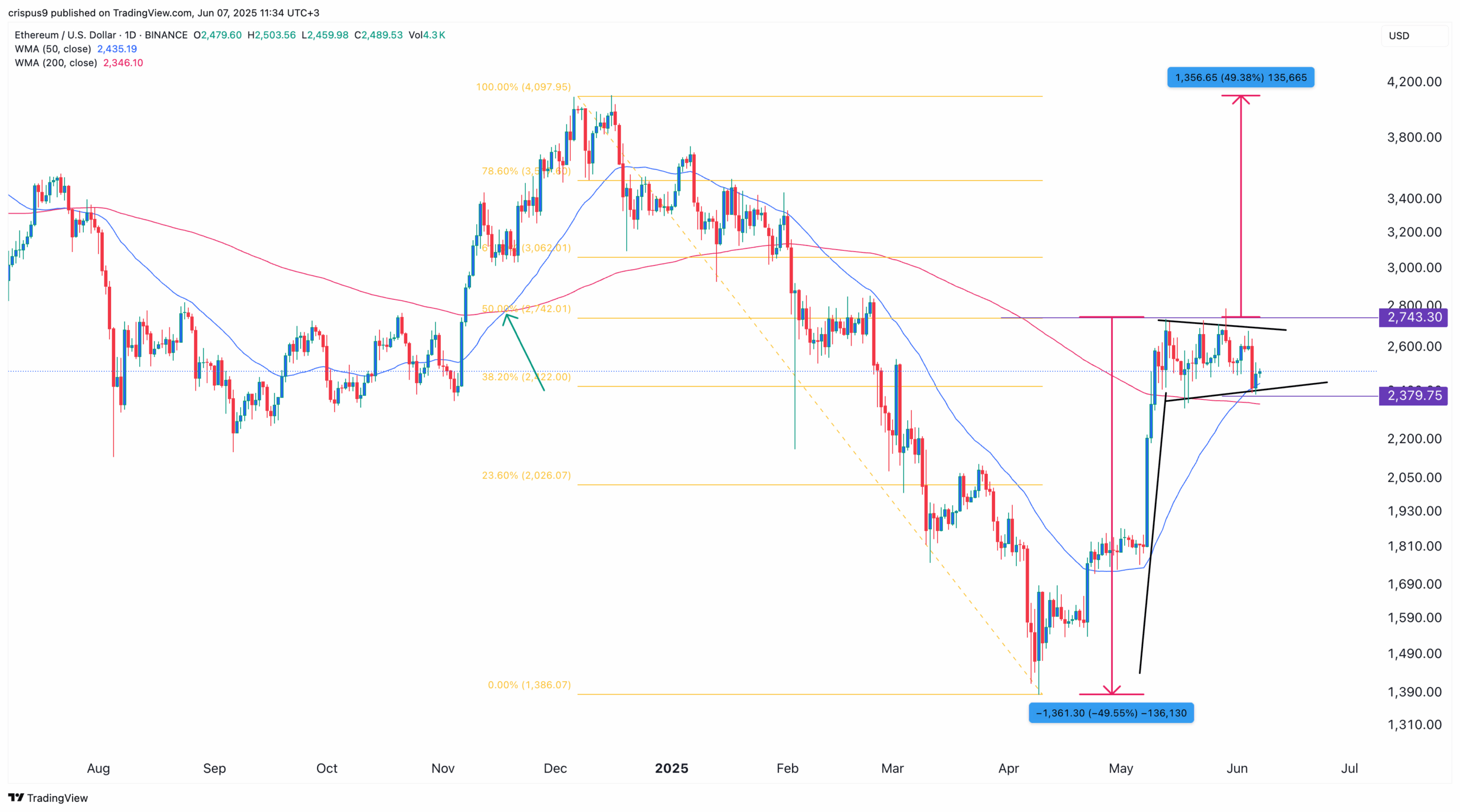
Ethereum price eyes breakout, ETHA ETF nears $5b milestone
Ethereum price may be on the verge of a bullish breakout to $4,000 after forming a bullish flag and a…
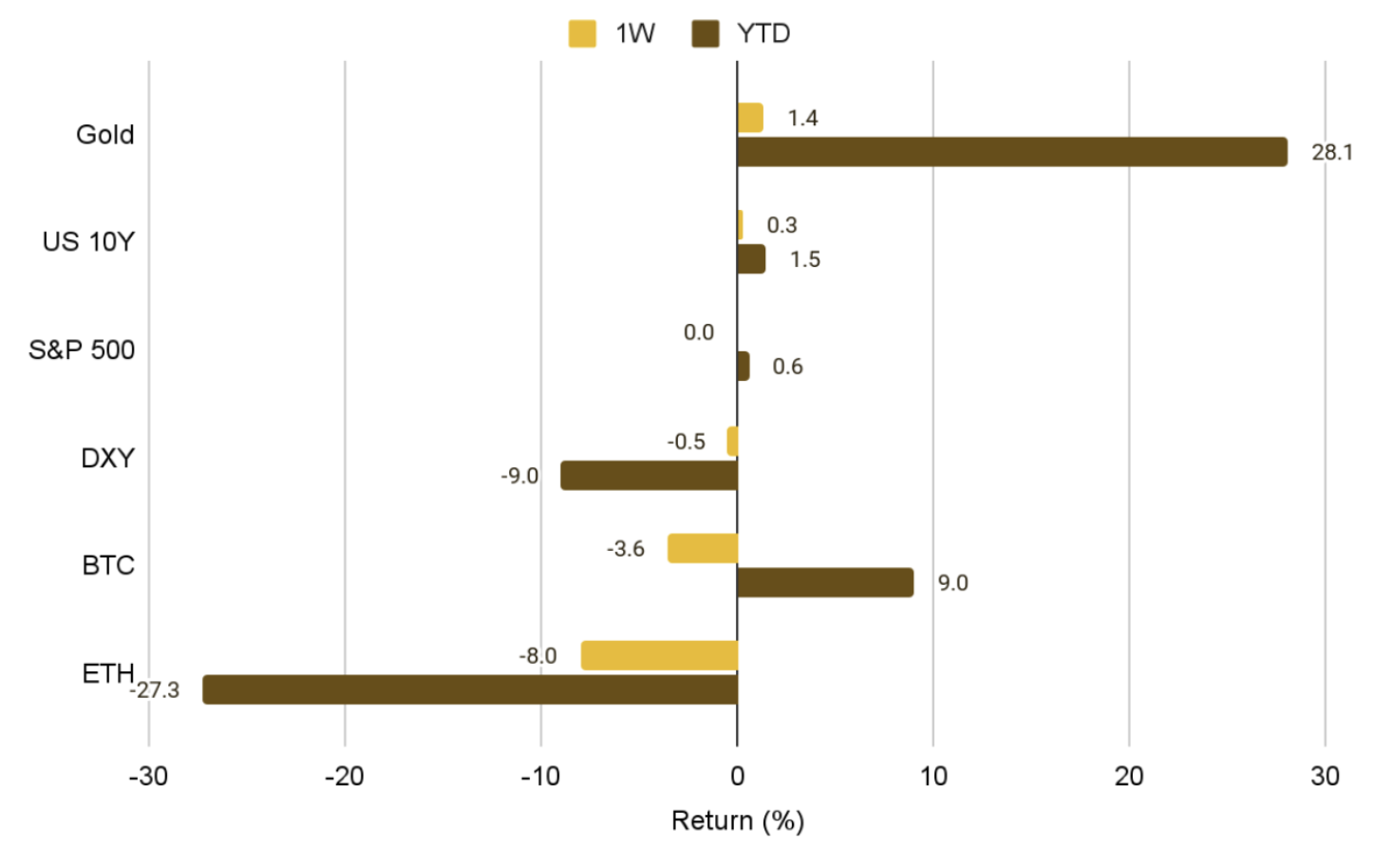
Bitcoin, Ethereum going mainstream as JPMorgan, SEC open doors: Binance Research
Binance Research highlighted several major developments that suggest that crypto is breaking into mainstream finance. Crypto is no longer on…


